Cabbage benefits
Check Out Nine Stunning Cabbage Health Benefits
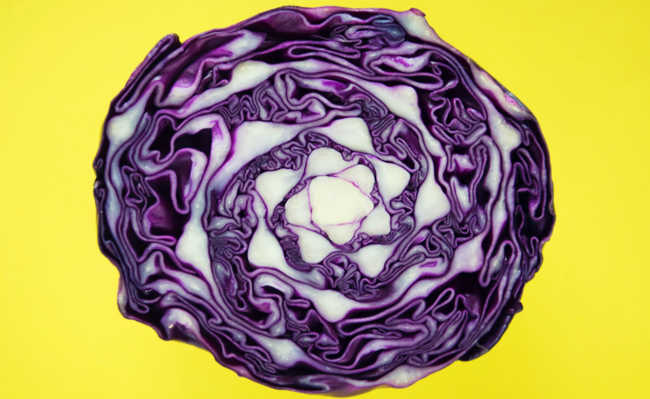
Cabbage is a vegetable belonging to the genus Brassica, the same as broccoli, cauliflower and kale. It is found in red, purple, white and green, and its leaves can be wrinkled or smooth.
Cultivated around the world for thousands of years, cabbage can be eaten in a variety of dishes, including sauerkraut, kimchi and coleslaw. It provides a number of health benefits, such as helping to control inflammation and heart health. Check out:
Cabbage benefits
1. Nutrient source
Cabbage has very few calories and an impressive amount of nutrients. Only ONE cup (89 grams) of raw green cabbage contains:
- Calories: 22
- Protein: 1 gram
- Fiber: 2 grams
- Vitamin K: 85% of the Recommended Daily Intake (RDI)
- Vitamin C: 54% of the RDI
- Folate: 10% of the IDR
- Manganese: 7% of the IDR
- Vitamin B6: 6% of the RDI
- Calcium: 4% of the IDR
- Potassium: 4% of the IDR
- Magnesium: 3% of the IDR
Cabbage also contains small amounts of other micronutrients, including vitamin A, iron and riboflavin. As you can see from the list above, it is rich in vitamin B6 and folate, both of which are essential for many important processes in the body, including metabolism and nervous system function.
In addition, cabbage is high in fiber and contains powerful antioxidants, including polyphenols and sulfur compounds (which, unfortunately, are responsible for the gas that eating cabbage causes in some people).
To know the importance of antioxidants, take a look at the article: "Antioxidants: what they are and what foods to find them in".
2. Helps keep inflammation under control
Inflammation is not always a bad thing, as the body depends on the inflammatory response to protect itself against infections and speed healing. Acute inflammation is a normal response to an injury or infection.
However, chronic inflammation (occurring over a long period of time) is associated with many problems, including heart disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease. And cabbage, being a cruciferous vegetable, can help reduce this type of inflammation (see study about it here: 1).
A study that included more than 1,000 Chinese women showed that those who ate the most cruciferous vegetables had considerably lower levels of inflammation compared to those who ate the smallest amounts.
Sulforaphane, kaempferol and other antioxidants found in cruciferous vegetables such as cabbage are probably mainly responsible for the anti-inflammatory effect (see studies about it here: 2, 3).
3. Rich in Vitamin C
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays many roles in the human body. It is essential for the production of collagen, a protein that gives the skin flexibility and is essential for the proper functioning of bones, muscles and blood vessels.
In addition, vitamin C helps the body absorb non-heme iron, the type of iron found in plant foods.
Vitamin C is also a powerful antioxidant, and has been extensively studied for its potential cancer-fighting qualities. It protects the body from damage caused by free radicals, which have been linked to many chronic diseases, including cancer (see study on this: 4).
- What are iron rich foods?
According to one study, the risk of lung cancer decreases by 7% for every 100 mg daily increase in vitamin C intake.
Green and red cabbage are excellent sources of this potent antioxidant, but red cabbage contains about 30% more.
One cup (89 grams) of chopped cabbage provides 85% of the recommended daily allowance of vitamin C, which is the same amount found in a small orange.
4. Improves digestion
Cabbage is very rich in insoluble fiber, a type of carbohydrate that cannot be broken down in the intestines and so helps keep the digestive system healthy by adding bulk to the stool and promoting regular bowel movements.
What's more, cabbage is a prebiotic rich in soluble fiber, which increases the number of beneficial bacteria in the gut such as Bifidobacteria it's the lactobacilli (Check out the study about it here: 5). These bacteria play important roles, such as protecting the immune system and producing essential nutrients, such as vitamins K2 and B12 (see studies about it here: 6, 7).
Eating cabbage is an excellent way to keep your digestive system healthy (if you suffer from gas formation, there are ways to prepare cabbage that will alleviate the problem. There are several recipes on the internet with tips on how to get the gas out of cabbage).
5. Good for the heart
Red cabbage contains powerful compounds called anthocyanins. They give this delicious vegetable its vibrant purple color.
Anthocyanins are plant pigments that belong to the flavonoid family. Many studies have found a link between eating foods rich in this pigment and a reduced risk of heart disease.
In a study that included 93,600 women, researchers found that those with a higher intake of anthocyanin-rich foods had a much lower risk of having a heart attack.
Another analysis of 13 observational studies that included 344,488 people had similar results. Increasing flavonoid intake by 10 mg per day was found to be associated with a 5% lower risk of heart disease.
Increasing the intake of anthocyanins in the diet also reduced blood pressure and the risk of coronary artery disease (see studies on this here: 8, 9). Cabbage contains over 36 different types of potent anthocyanins, making it an excellent choice for heart health (see study about it here: 10).
6. It can lower blood pressure
High blood pressure affects more than a billion people worldwide and is a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke. Doctors often advise patients with high blood pressure to reduce their salt intake. But recent evidence suggests that increasing dietary potassium is also important for lowering blood pressure.
Potassium is an important mineral and electrolyte that the body needs to function properly. One of its main jobs is to help regulate blood pressure, neutralizing the effects of sodium in the body. The mineral helps to excrete excess sodium through the urine. It also relaxes blood vessel walls, which lowers blood pressure.
Although sodium and potassium are important for health, modern diets tend to be too high in sodium and too low in potassium. Red cabbage is an excellent source of potassium, providing 12% of the RDI in a 2 cup serving (178 grams). So eating cabbage is a delicious way to reduce high blood pressure.
7. Can help reduce cholesterol level
Cholesterol is a waxy, fatty substance found in every cell in the body. Some people think that all cholesterol is necessarily bad, but there is also so-called 'good cholesterol', which is essential for the proper functioning of the body.
Critical processes depend on cholesterol, such as proper digestion and the synthesis of hormones and vitamin D. However, people who have high cholesterol also tend to have an increased risk of heart disease, especially when they have high levels of LDL cholesterol, the "bad".
In that case, cabbage can be an ally, as it contains two substances that help reduce bad cholesterol levels. One is soluble fiber.
Soluble fiber has been shown to help lower “bad” LDL cholesterol levels by binding to this type of cholesterol in the intestine and preventing it from being absorbed into the blood.
A large analysis of 67 studies showed that when people ingest 2 to 10 grams of soluble fiber a day, they experience a small but significant reduction in LDL cholesterol levels - about 2.2 mg per deciliter.
Cabbage is a good source of soluble fiber. About 40% of the fiber found in cabbage is soluble.
Another class of substances present in cabbage that help reduce bad cholesterol are phytosterols. They are plant compounds structurally similar to cholesterol, and therefore "trick" the body, blocking the absorption of cholesterol in the digestive tract.
Increasing phytosterol intake by 1 gram per day reduces LDL cholesterol concentrations by up to 5% (see study about it here: 11).
8. Vitamin K source
Vitamin K is a set of fat-soluble compounds that play many important roles in the body, being divided into two main groups:
- Vitamin K1 (Phylloquinone): Found primarily in plant sources;
- Vitamin K2 (menaquinone): Found in animal sources and in some fermented foods. It is also produced by bacteria in the large intestine.
Cabbage is a great source of vitamin K1, providing 85% of the recommended daily amount in a single cup (89 grams). This vitamin has as one of its main functions acting as a cofactor of enzymes responsible for blood clotting.
Without vitamin K, the blood would lose its ability to clot properly, increasing the risk of excessive bleeding.
9. It's very easy to add to your diet
In addition to being super healthy, the cabbage is delicious. It can be eaten raw or cooked and added to a wide variety of dishes such as salads, soups, stews and fermented, acting as a great prebiotic - when raw - or probiotic - when fermented.
No matter how you prepare cabbage, adding this cruciferous vegetable to your plate is a tasty way to benefit your health.










